BED BUGS
BEDBUG FACTS
Bedbugs develop through five nymphal instars before developing into adults, and with each stage requiring a blood meal in order to moult into the next instar. Bedbugs are not disease carriers but their blood feeding can cause severe irritation in some people, resulting in loss of sleep, lack of energy and listlessness. In addition, presence of bed bugs are also a source of stress and can affect the mental health of hosts.
How can bed bugs get into my home?
Bed bugs cannot fly, therefore they either crawl or be passively transported in clothing, on or in luggages, used furniture, books, and other objects used as harbourages. They can come from other infested areas or hitch a ride in luggage, purses, backpacks, or other items placed on soft or upholstered surfaces. They can travel between rooms in multi-unit buildings, such as apartment complexes and hotels.

METHOD OF TREATMENT FOR BED BUGS
Bedbugs are smart. As a survival instinct, bed bugs are elusive. They know to stay out of view during the daytime, hiding in mattress crevices, box springs, baseboards, behind electrical switchplates, in picture frames, and even behind wallpaper. But at night-time, the carbon dioxide we exhale often tempts them out of their hiding spots.
Bedbugs resist pesticides as they developed a natural resistance to pesticides quickly. Chemical rotation together with Integrated Pest Management (IPM) methods are being utilized to slow down the development of bed bed bug resistance.
Treatment of bedbug infestation is a combination of hygiene management, heat treatment and effective and safe chemical treatment program. Before treatment, a thorough inspection is needed to determine the extent of the infestation and planning to safely execute control strategies.
For chemical control, residual spray is used to treat the infested area and treatment should be directed at all the harbourages and where bedbugs are found.
Chemical control can be highly effective, if you detect the infestation in its early stages, chemicals can eradicate bed bugs quickly and reliably. Moreover, the combination of a broad spectrum pyrethroid insecticide (PY) and insect growth regulator (IGR) for quick knockdown and residual insecticidal activity where you can effectively hit bed bugs over time, and throughout every stage of their life-cycle.
Residual insecticides act as a barrier against future bedbug infestations. It can help prevent future infestations. While the continued presence of protection barrier in the home is not an ideal solution for everyone, it undeniably offers long-term protection.
Chemical control is cost effective and often slightly less expensive than the bedbug heat treatment option. However, a chemical control requires time, preparation and careful planning such as thoroughly prepare infested areas, removing as many barriers as possible to ensure the chemicals reach where the bedbugs are hiding.
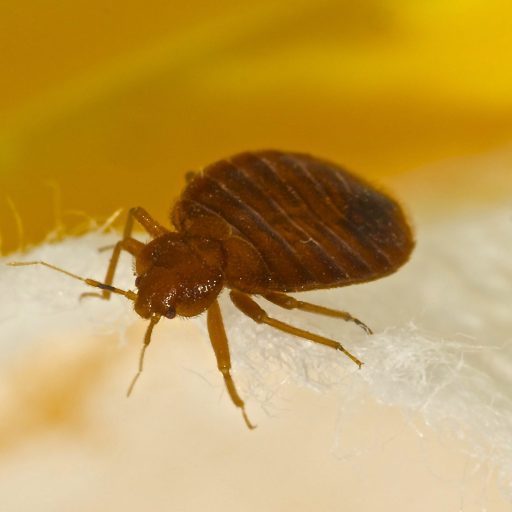

SIGNS OF BED BUG INFESTATION
A bed bug infestation can be identified by:
- Dark/ small reddish-brown fecal spots on your wall, headboard, mattress, beddings and clothes.
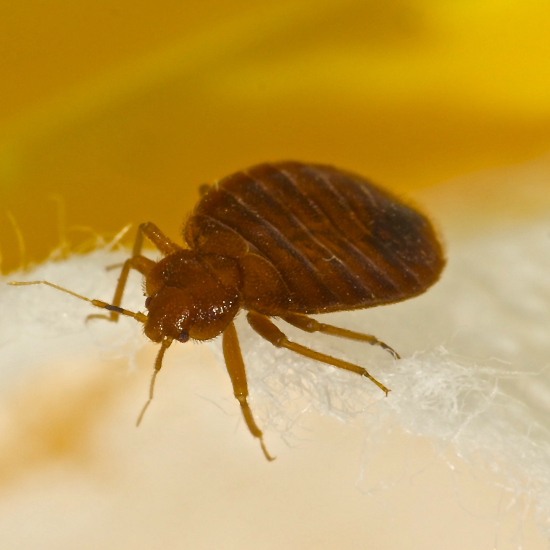
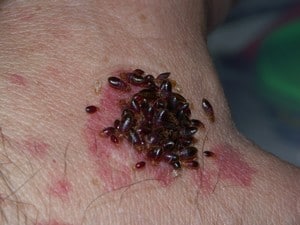
- Live bedbugs -They are small about the size of an apple seed, reddish-brown parasitic blood sucking insects measuring around 4-5mm long (adult).
- Bedbug molt skins – their eggs, empty egg shells or the bedbugs itself.
- Bites on the body -as bed bugs feed, they inject a salivary secretion into the wound to prevent coagulation. Some people have no reaction to bedbug bites, while others experience an allergic reaction that can include severe itching, blisters or hives.
- Sweet scent – An offensive, sweet, musty odor from the bugs’ scent glands
TYPES OF BEDBUGS
There are two main bedbug types, Common Bedbugs, Cimex lectularius and Tropical Bedbugs, Cimex hemipterus. The most common bedbug species found in South East Asia are the Tropical Bed Bugs, Cimex hemipterus. There are other species in the Cimex genus that feed on bats and birds. But, none of these feed on humans.
Although bedbugs aren’t known to spread disease, they can cause other a variety of negative physical health, mental health and economic issues. Bedbugs bite and feed on human can cause severe irritation in some people, resulting in loss of sleep, lack of energy and listlessness. In addition, presence of bed bugs are also a source of stress and can affect the mental health of hosts. Bedbug bites can lead to anxiety, sleeplessness and even secondary infections, but there have been no reported cases of bedbugs transmitting disease to humans.
However, bedbugs do harbor human pathogens. At least 27 viruses, bacteria, protozoa and more have been found in bedbugs, although these microbes do not reproduce or multiply within the insects.
To effectively curb the current bedbug resurgence in Asia, it is necessary to implement proactive bedbug monitoring programs in areas that are currently experiencing a bedbug resurgence.


 CHEMICALS
CHEMICALS